
اگر به یک وب سایت یا فروشگاه رایگان با فضای نامحدود و امکانات فراوان نیاز دارید بی درنگ دکمه زیر را کلیک نمایید.
ایجاد وب سایت یادسته بندی سایت
محبوب ترین ها
پرفروش ترین ها
پر فروش ترین های فورکیا
 پکیج حرفه ای کسب درآمد میلیونی ( تضمینی و تست شده)
پکیج حرفه ای کسب درآمد میلیونی ( تضمینی و تست شده) دانلود طرح لایه باز اعلامیه ترحیم (11) (دانش یاران)
دانلود طرح لایه باز اعلامیه ترحیم (11) (دانش یاران) دانلود "کتاب صدای خود را آزاد کنید"pdf+فایلهای تمرینی
دانلود "کتاب صدای خود را آزاد کنید"pdf+فایلهای تمرینی دانلود کتاب صوتی ترک آسان سیگار
دانلود کتاب صوتی ترک آسان سیگار دانلود کتاب صوتی کلیدر (مجموعه کامل)
دانلود کتاب صوتی کلیدر (مجموعه کامل) پکیج صداسازی متود CVT
پکیج صداسازی متود CVT نمونه سوالات انباردار رشته حسابداری فنی حرفه ای | کاردانش با جواب
نمونه سوالات انباردار رشته حسابداری فنی حرفه ای | کاردانش با جواب کتاب آموزش زبان آلمانی A-Grammatik به همراه پاسخ نامه و فایل های صوتی کتاب
کتاب آموزش زبان آلمانی A-Grammatik به همراه پاسخ نامه و فایل های صوتی کتاب کتاب معلم Nuevo prisma libro de profesor (A2)
کتاب معلم Nuevo prisma libro de profesor (A2) کسب درآمد اینترنتی 300000 تومان در خانه در کمتر از 30 دقیقه
کسب درآمد اینترنتی 300000 تومان در خانه در کمتر از 30 دقیقه نمونه سوالات اکسل همراه با جواب pdf
نمونه سوالات اکسل همراه با جواب pdf دانلود کتاب صوتی برادران کارامازوف (جلد اول و دوم بصورت کامل)
دانلود کتاب صوتی برادران کارامازوف (جلد اول و دوم بصورت کامل) ترمینولوژی حقوق دکتر جعفر لنگرودی
ترمینولوژی حقوق دکتر جعفر لنگرودی نمونه اجاره نامه مسکونی تجاری همراه با اصل فایل(دانش یاران)
نمونه اجاره نامه مسکونی تجاری همراه با اصل فایل(دانش یاران)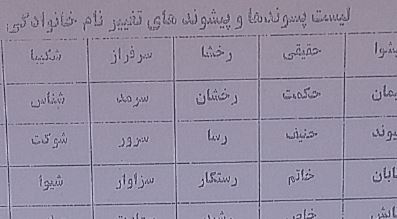 لیست پسوند و پیشوند فامیلی مورد تایید سازمان ثبت احوال
لیست پسوند و پیشوند فامیلی مورد تایید سازمان ثبت احوال کتاب مغناطیس جذب دختر
کتاب مغناطیس جذب دختر کتاب صوتی هنر شفاف اندیشدن با صدای عادل فردوسی پور
کتاب صوتی هنر شفاف اندیشدن با صدای عادل فردوسی پور علائم گرافیکی تحلیل سایت فتوشاپ
علائم گرافیکی تحلیل سایت فتوشاپ دانلود کتاب صوتی جان شیفته (مجموعه کامل)
دانلود کتاب صوتی جان شیفته (مجموعه کامل) کتاب حقوق مدنی 6 دکتر ناصر کاتوزیان
کتاب حقوق مدنی 6 دکتر ناصر کاتوزیان آموزش فعال کردن چشم سوم
آموزش فعال کردن چشم سوم جزوات و حل تمرینات و نمونه سوالات امتحانی درس تحلیل سیستم های انرژی رشته های فنی مهندسی
جزوات و حل تمرینات و نمونه سوالات امتحانی درس تحلیل سیستم های انرژی رشته های فنی مهندسی ساخت ربات های تریدر (معامله گر) با نرم افزار Forex Strategy Builder بدون نیاز به هیچ علم تکنیکال یا علم برنامه نویسی
ساخت ربات های تریدر (معامله گر) با نرم افزار Forex Strategy Builder بدون نیاز به هیچ علم تکنیکال یا علم برنامه نویسی کتاب آموزش خیاطی انواع لباس مجلسی
کتاب آموزش خیاطی انواع لباس مجلسی دانلود کتاب صوتی دروغگویی روی مبل
دانلود کتاب صوتی دروغگویی روی مبل طرح جابر بازیافت
طرح جابر بازیافت دانلود طرح لایه باز تقدیر نامه و لوح سپاس(18)( دانش یاران)
دانلود طرح لایه باز تقدیر نامه و لوح سپاس(18)( دانش یاران)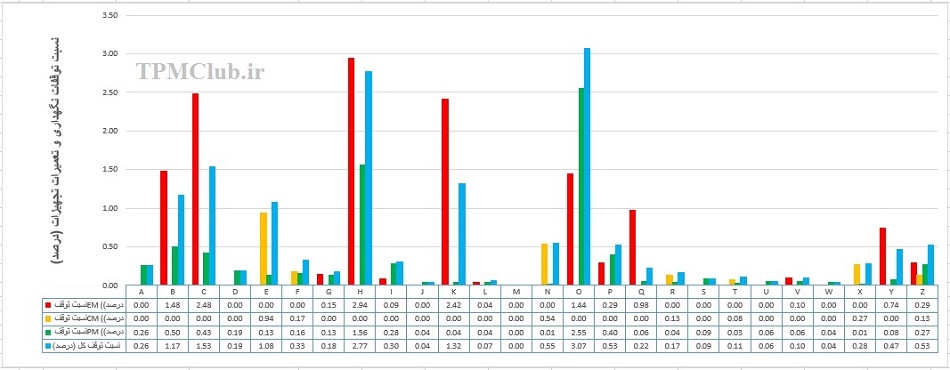 فرم اکسل شاخص کل توقفات نت (پارتو توقفات فنی)
فرم اکسل شاخص کل توقفات نت (پارتو توقفات فنی)پر بازدید ترین های فورکیا
 فروش فیلتر بورسی استریکلی فقط 75 هزار تومان
فروش فیلتر بورسی استریکلی فقط 75 هزار تومان کسب درآمد اینترنتی 300000 تومان در خانه در کمتر از 30 دقیقه
کسب درآمد اینترنتی 300000 تومان در خانه در کمتر از 30 دقیقه کسب درآمد روزانه حداقل یک میلیون تومان ! کاملا حلال و واقعـی !!
کسب درآمد روزانه حداقل یک میلیون تومان ! کاملا حلال و واقعـی !! مجموعه ی آموزش تعمیر لامپ کم مصرف (از مبتدی تا پیشرفته)
مجموعه ی آموزش تعمیر لامپ کم مصرف (از مبتدی تا پیشرفته) دانلود پکیج درآمدزایی 400هزارتومن در 40دقیقه (مخصوص شرایط تورم 50 درصدی)
دانلود پکیج درآمدزایی 400هزارتومن در 40دقیقه (مخصوص شرایط تورم 50 درصدی) کسب و کار اینترنتی در منزل
کسب و کار اینترنتی در منزل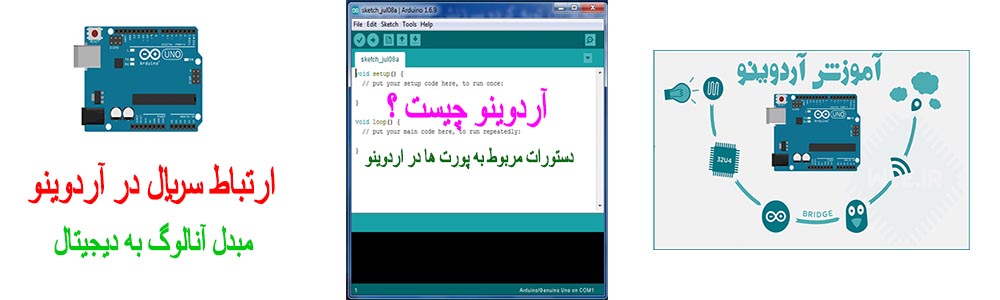 آموزش برنامه نویسی آردوینو
آموزش برنامه نویسی آردوینو آموزش رایگان کسب درآمد از سایت الیمپ ترید ( olymp trade )
آموزش رایگان کسب درآمد از سایت الیمپ ترید ( olymp trade )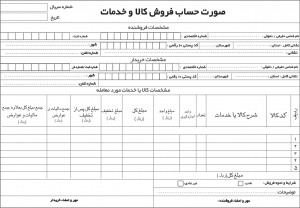 دانلود نمونه فاکتور آماده با فرمت ورد - اکسل و عکس
دانلود نمونه فاکتور آماده با فرمت ورد - اکسل و عکس آموزش ساخت بازی بدون دانش برنامه نویسی و طراحی سه بعدی مبتدی تا پیشرفته با نرم افزار
آموزش ساخت بازی بدون دانش برنامه نویسی و طراحی سه بعدی مبتدی تا پیشرفته با نرم افزار اموزش کسب درامد از اینترنت روزانه ۳میلیون تومان تضمینی و تست شده
اموزش کسب درامد از اینترنت روزانه ۳میلیون تومان تضمینی و تست شده درامدزایی در خواب! (تعجب نکنید! بخوانید)
درامدزایی در خواب! (تعجب نکنید! بخوانید) مدار داخلی واکی تاکی(اموزش ساخت)
مدار داخلی واکی تاکی(اموزش ساخت) کتاب افزایش ممبر کانال تلگرام
کتاب افزایش ممبر کانال تلگرام دانلود100% رایگان نرم افزار تبلیغات در تلگرام + آموزش کامل و فیلم آموزشی
دانلود100% رایگان نرم افزار تبلیغات در تلگرام + آموزش کامل و فیلم آموزشی روش اصلی موفقیت در کنکور و آزمون ها(پزشکی، حقوق، مهندسی، نمونه و تیزهوشان) با پکیج کنکورپلاس
روش اصلی موفقیت در کنکور و آزمون ها(پزشکی، حقوق، مهندسی، نمونه و تیزهوشان) با پکیج کنکورپلاس چگونه هر شخصی را عاشق خود کنیم ارزان
چگونه هر شخصی را عاشق خود کنیم ارزان برنامه ساز اندروید و کسب درآمد بالا
برنامه ساز اندروید و کسب درآمد بالا ثروتمند شدن حق شماست !! امتحان کنید!!!
ثروتمند شدن حق شماست !! امتحان کنید!!! ساده ترین و پردرآمد ترین کسب و کار در اینترنت تا لحظه درآمد با شما همراه خواهیم بود
ساده ترین و پردرآمد ترین کسب و کار در اینترنت تا لحظه درآمد با شما همراه خواهیم بود حل تمارین دینامیک سازه
حل تمارین دینامیک سازه کسب درآمد میلیونی از وبلاگ
کسب درآمد میلیونی از وبلاگ دانلود پکیج درآمدزایی 400 هزارتومن در 40 دقیقه (مخصوص شرایط تورم 50 درصدی)
دانلود پکیج درآمدزایی 400 هزارتومن در 40 دقیقه (مخصوص شرایط تورم 50 درصدی) دانلودپکیج ربات فالوور و لایک نامحدود و رایگان اینستاگرام(فوق حرفه ای)
دانلودپکیج ربات فالوور و لایک نامحدود و رایگان اینستاگرام(فوق حرفه ای) مجموعه "صفر تا صد راه اندازی کارگاه جوراب بافی"
مجموعه "صفر تا صد راه اندازی کارگاه جوراب بافی" کسب در آمد میلیونی از اینترنت (نسخه ی پیشرفته) 80 درصد تخفیف
کسب در آمد میلیونی از اینترنت (نسخه ی پیشرفته) 80 درصد تخفیف اندیکاتور R & S جهت کسب درآمد از سایت الیمپ ترید
اندیکاتور R & S جهت کسب درآمد از سایت الیمپ تریدپیوند ها
Introduction: In recent years, one of the topics which absorbed great volume of psychological researches welfare. In the last two decades, research on happiness have risen dramatically. ARGYLE (1995) believes, if happiness is just the opposite of depression, there is no need to measure and evaluate it. Because the depression is well known. He believes that, three main components of happiness are: positive emotion, satisfaction from life and lack of negative excitements including depression and anxiety. He and his colleagues found that positive relations with others, purpose in life, personal growth, loving others and nature are also part of happiness. Myers & DIENER (1995), say: when people were asked, who is happy person? In response, they point to a supportive network of interpersonal relationship in a culture, who have positive and optimistic interpretation from everyday events. Components of happiness are: first, affective and emotional component, which makes happy people to be in happy mood always. Second, is social component, social relationship with others, follows increase in social support. Third component is cognitive, which causes the happy fellow to have his own thinking and information processing and interprets the current events in a way that brings his optimism. There is so much interest among researchers to determine what makes people happy. Although researches have been concentrated on demographic factors and other economical social variables, but today it is thought that some people are happier than others, because of their personality traits. Most of the researches in connection with happiness following this study just like BREBNER & MARTIN (1995), CHAN (2004), FURNHAM & CHAN (1997), HILL & ARGYLE (2001) and LEVY& LEVY (2005) have confirmed these associations. However, other personal dimensions were not considered as extraversion and extreme mental depression in researches. ASGARI (2014), investigated about theoretical social acceptance with the help of theories of behavioral analysis. EBRAHIMPOUR, ZAHED and ELYASI (2014), considered the role of managers social utility in organizational performance as significant. SHABANI, DELAVAR, BELOUKI and MAMSHARIFI (2013), reported about the relationship of self-efficacy, social support and optimistic in mental well-being forecast in order to develop a structural model of students. In 1960 decade, American poll organizations began asking questions about happiness and satisfaction. In 1984, DIENER, did the same work and it was updated in 1999. GALLUP, MORT and other poll organizations were conducting other surveys, not only in America but also in Europe and common market countries. In the theories called as final goal, there is a belief as happiness is necessary and welfare will be achieved when, individuals cover their goals based upon values and needs. Those fellows who are assuming their goals as more important and consider more success possibility to reach them, will feel more happiness and welfare. But those who have less happiness, will feel more prejudice. It seems that individuals efficient move toward their goals, is the reason for positive changes in their happiness. (DIENER 2005). Self-efficacy is one of the important structures in social cognitive theory of BANDURA. And it means the person has confidence and belief toward his own abilities in thoughts control, feelings, activities and also his effective operation in stressed activities. Therefore, on individual real operation, emotions, selections, effective events inhabitation, organize and run the needful operations in a direction of achieving and scoring performance level and finally the rate of effort which person spends on activity is effective (STEPHENS, 2002). Self-efficacy as personality variable, has important role in individual encounter with life issues. And as property of predictor personality can be effective factor in in train and education opportunities. Durability in assignment performance, high operation level and proportional with abilities, active search in new successes, challenge assume of problems, effective collision with the events and conditions, issue decoding ability and appropriate use from analytical thought, failure courage, selecting more challengeable tasks, selecting higher goals, commitment and stability to reach them and self- mastery when withdrawal is necessary are the characteristics of self- efficacy individuals (BANDURA, 2006). One more variable for individual recognize dimension is social utility. Tendency to be eligible is a common need among all humans. All people, naturally like to be accepted by others and try to gain it (SEDGH POUR, MAHMOUDIAN & SOLEIMANIAN, 2010). Social utility is just like continuum, in one of its end, there are some people with high level of social utility who will change their own ideas and experiences in interviews and in replying to the questions. And in the other end, there are some people with less level of social utility who will never change their own ideas and experiences. Considering the above statement, the main objective of the present study is to investigate the role of social desirability predictor and self-efficacy in happiness of girl students in high school section in BANDAR ABAS city. In other words, this research seeks to ensure that social desirability and self –efficacy predicts how much of happiness variances in female students in BANDAR ABAS city? Method: The recent study is a description of solidarity kind which has been implemented as square form has been paid to study the role of social desirability and self-efficacy in happiness of female students in high school section in BANDAR ABAS city. And also self-efficacy and utility are considered as independent variable, and happiness is considered as depended variable. According to the purpose of the study the statistical society including all female students who are studying in section one of education ministry of BANDAR ABAS city in the year 2015-2016 and, and they are 1790 people and final sample was on the basis of the MORGAN table. So they were selected 316 people with simple random selection system. But at the end, 300 questionnaire were returned and was used statistically. Research tools: Oxford happiness questionnaire: a list of 29 items of oxford happiness was made for the first time by ARGYL and LU. After some years, ARGYL has revised the scale and now it is widely used in the UK. This with 29 words was set in LIKERT four degrees scale. And was numbered as (3, always, 2, sometimes, 1, rarely, 0, never). Scores below 22 (less happiness), scores 22 to 44 (medium), grades 44 to 68 (above joy), and grades 68 to 87 (very happy). FARANSIS in a cross-cultural study in Britain, USA, Australia and Canada reported the alpha 0/89, 0/90, 0/89 and 0/0 respectively (ALIPOUR and AGHAH HARRIS, 2008). Self- efficacy questionnaire of SHERER and staff: This questionnaire has 17 questions. For every self-efficacy scale question, 5 answers were suggested. For this reason, each question gets 5 points. Question numbers 1, 3, 8, 9, 13 and 15 from right to left, points will be raised. And other questions in reverse order, from left to right, points will be increased. The total score will be achieved through sum of the question scores. Those who get one standard deviation up or down the average gain, will be defined as up and down self-efficacy people (SEIF and MARZOGHI, 2009). Social desirability questionnaire: This questionnaire with the goal to measure the rate of social desirability of individuals with 9 questions were used. It was built by KAR and was translated by REZVANI (1997). Scoring system and result interpretation to select each correct answer for numbers 1, 3, 4, 6, 9, give one point to yourself. To select each wrong answer for numbers 2, 5, 7, 8, give one point to yourself. How much your total score is up, shows your tendency toward answer style which is called as social acceptability. The reliability of this study, by internal consistency system of CRONBACH`s alpha was calculated to 0/66 percent. And this is acceptable finishing for this questionnaire (EBRAHIMPOUR, ZAHED and ELYASI, 2014). Method of data analysis: To analyze the statistical data of the KOLMOGOROV SMIRNOV tests to check the normality of the data distribution and PEARSON correlation and multiple regression was used step by step. Findings: Some of the necessary assumptions for doing the PEARSON correlation analysis and multiple regression: Normality of the data distribution which was confirmed by KOLMOGOROV SMIRNOV. Because the significant levels of both variables are smaller than (p<0/05). These variables will not follow normal distribution but due to the high volume of samples (more than 150 people), even though, data distribution related to studied variables is not normal, we can use PERASON correlation coefficient for relation research. (table1) Statistics of normality test of KOLMOGOROV SMIRNOV: __________________________________________________________ Residuals KOLMOGOROV SMIRNOV Statistics value - liberty degree - significant level __________________________________________________________ Social desirability 2/030 300 0/01 __________________________________________________________ Self-efficacy 3/240 300 0/01 __________________________________________________________ Happiness 0/976 300 0/29 Based on the data analysis, it has been indicated that PEARSON correlation coefficient between two social desirability variables and happiness is equal to r=0/348, p<0/001, with attention to a significant level, theory of will be rejected, because of no relation. And therefore, there is significant relationship between social desirability and happiness. But according to PEARSON correlation coefficient, between two self- efficacy variables and happiness is (r = 0/348, p <0/001), and with attention to significant a significant level, theory of will be accepted, because of no relation. And therefore, there is no significant relationship between self-efficacy and happiness. Table 2) correlation coefficients between variables Independent variable Dependent variable correlation coefficient Significant level. Social desirability happiness 0/348 0/01 Self-efficacy happiness 0/079 0/17 According to table 3, and based on the results of the stepwise regression, social desirability is the first priority in happiness predict. And will predict the happiness positively. And will have increase effect in happiness variance (Beta=0/348, p<0/005). But self-efficacy will not predict any change in happiness. And will not have increase effect in its variance (Beta=0/393, p>0/005). Finally, based on R^2value, adjusted 11/8 percent from variance change in happiness variation will be explained by social desirability. Table 3- multiple regression table Variable Criterion: Happiness Not Standard coefficients Standardize coefficients t P Factor B Mistake value Beta Fixed 71/058 2/044 34/772 * 0/001 Predictor variables Social desirability 2/187 0/341 0/348 6/416 * 0/0001 Self-Efficacy 0/950 0/089 0/393 1/648 0/10 Discussion and conclusion: This study aimed to investigate the role of social desirability predictor and self-efficacy in happiness of female students in high school section of BANDAR ABAS city. The results also showed that there is direct relationship between social desirability and happiness. This means that with increase in social desirability rate of students, their happiness will increase also. This finding is consistent with similar studies including AGHABABAEE, MOHAMMADTABAR and SAFARI NIYA (2014), the social behavior of the higher piety and honesty- humility and levels of narcissism, psychopathy were related, and reported a significant relationship between them. SARMADI SOLTAN, ZAREEE MIANKELLI and SALIMI BAJESTANI (2014), also reported a relation between ecological and social desirability. SHABANI, DELAVAR, BULOUKI and MAM SHARIFI (2013) also reported a relation between social support and happiness. Social support and understanding this issue by students is an effective factor in prevention from people`s involvement in psychological trauma such as depression, anxiety and stress. And we can say, those who have support and social desirability will have more health and happiness. Will form stronger and better social networks around themselves. And have healthier life style. On account of this hypothesis, we can say, when people see themselves with high popularity in society and are accepted by social groups, are more satisfied in life, will have more pleasure from being with others, and isolate the effect of anxiety and depression. As a result, happiness rate in these people will increase. The results also show that, between self-efficacy and happiness of female students in high school section in BANDAR ABAS, there is no significant relationship. That is, no relationship between students `s self-efficacy and their happiness. This finding with researches like: ABASI and HOJATI (2010) reported that happiness will have effect in increasing the self-efficacy of the students. ESMAILI FAR, SHAFI ABADI and AHGHAR (2012), reported a significant relationship between self-efficacy and happiness, and announced that self-efficacy will have significant role in happiness predict. SHABANI, DELAVAR, BULOUKI and MAMSHARIFI (2013), reported that when self-efficacy and optimism have shown significant and direct effect on happiness, is inconsistent. But to explain the result of this theory, we can say that the lack of association between self-efficacy and happiness in this study is may be due to the lack of suitable fill out of questionnaire by students and enough description were not given to the responders to prevent their biases or there was not required accuracy in selecting suitable model. It means that the suitable sample was not selected. Resources: EBRAHIMPOUR, HABIB, ZAHED, ADEL, ELYASI and AZIM (2014), role of social desirability of managers and organizational performance, second national conference of modern management science ESMAILIFAR, NEDA, SHAFIABADI, ABDOLLAH and AHGHAR, GHODSI (2010), the share of self-efficacy in predicting happiness, ANDISHE journal, Vol. V, No 19, pp. 27-44 SEIF, DIBA, MARZOUGHI, RAHMATOLLAH, (2009), the relationship between epistemological beliefs and self-efficacy and academic performance of secondary school students in science class, DANESHVAR, RAFTAR, No. 33, pp. 1-14. - SARMADI SOLTAN, VAHID, ZAREEE MIYANKALI, FARSHAD and SALIMI BAJESTANI, HOSSEIN, (2012), the effectiveness of teaching life skills on talking and social desirability of students, Developmental Psychology, tenth year, No. 137, pp. 81-89 SHABANI, SOMAYEH, DELAWAR, BOLOUKI, AZADE and MAMSHARIFI, Ismail, (2013), Evaluation of self-efficacy, social support and subjective well-being optimistic forecasters to develop a structural model for students, studies in clinical psychology journal, Number VIII, second year, pp. 94-117. - SEDGHPOUR, SALEH, MAHMOUDIAN, Majid and SALMANIAN, HAMID REZA, (2010), study the effect of the teachings of the Quran on improvement of social acceptance, QORANIC Interdisciplinary Research Journal, Vol. II, No. VI, pp. 18-25. ASKARI, MOHSEN, (2014), the concept of social acceptance by the theories of behavioral analysis, the second National Conference of modern science management. - ALIPOUR, AHMAD and AGAH Harris, MOJGAN (2008), "The validity and Happiness Index, Oxford in Iranians", Iranian Journal of Psychologists, third year, No. 12, pp. 287- 298. - NESHAT DOUST, Hassan PALAHANG, FATEME BAHRAMI, (2008), TARBIYAT MOALEM University, master degree thesis, Esfahan, JAHAD DANESHGAHI Press. Argyle, M. (1995). Psychology and religion: An introduction. London: ROUTLEDGE. - BREBNER, J., & Martin, M. (1995). Testing for stress & happiness: The role of - Bandura, A. (2006). Adolescent development from an agnatic Perspective. In F. - Cheung, FM (2004). Use of western and Indigenously Developed Personality Test in Asia. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 53, 173-191. - DIENER. E. (1984). Subjective wellbeing. Psychology Bulletin, 95, 542-575. - DIENER. E., SUH, EM, Lucas, RE, & smith, HL (1999). Subjective wellbeing three decades of wellbeing. Psychological Bulletin, 125 (2), 276-302. DIENER. E. (2005). Frequently asked questions about subjective wellbeing - (Happiness and life satisfaction) ". A primer for reports and newcomers. http: // www . PSYCH. UIUC. EDIENER / FAA. Html - Hills, P., & Argyle, M. (2001). Emotional stability as a major dimension of Happiness. Personality and Individual Differences, 31 (8), 1357-1364. - FURNHAM, A., & Cheng, H. (1997). Personality & Happiness. Psychological Reports, 83, 761-762. - Levy, SS, & Levy, V. (2005). The exercise and self- esteem model in adult - MAYERS, DG, & DIENER, E. (1995), Who Is Happy? Psychological Science, 6, 10- 19. Stephens, J. (2002). Physical activity, mental health and personality trait in the USA and Canada: Evidence from four population surveys. Journal of sport Behavior, 20 (4): 465-477. ________________________________________ [1] Graduate Student, Educational Psychology, University of Bandar Abbas, Iran [2] Associate Professor of Psychology, University of Tehran, Bandar Abbas, Iran [3] . Happiness [4] . Argyle [5] . Myers & DIENER [6] . BREBNER & Martin [7] . Chan [8] . FURNHAM [9] . Hills [10] . Levy & Levy [11] .DIENER [12] .Gallup [13] .MORT [14] . DIENER [15] . Bandura [16] . Stephens [17] . FARANSIS